Saudi Arabia today is one of the fastest-growing markets in the world. The country’s economy is actively diversifying under the national Vision 2030 strategy, and mega-projects such as NEOM are creating massive demand for imported goods and technologies. However, entering this market is not simple: in order to participate in tenders and sign contracts, companies are required to obtain certification in accordance with national and international standards.
Main Regulatory Authorities
- SASO (Saudi Standards, Metrology and Quality Organization) – the main body responsible for standardization and certification in Saudi Arabia.
- SABER – an electronic platform for registration and certification of imported products.
- SFDA (Saudi Food and Drug Authority) – regulates food, pharmaceuticals, and medical devices.
- Saudi Customs – oversees product importation and requires certificates for customs clearance.
Key Certification Requirements
1. SASO Certificate of Conformity (CoC)The primary document for importing goods into the Kingdom. It confirms that products comply with national standards. Without it, shipments cannot clear customs.
2. Registration on the SABER Platform
Every product must be registered in the system, specifying its category, manufacturer, certificates, and test results.
3. Energy Efficiency and Water Efficiency Labels
Mandatory for household appliances, electronics, and plumbing products. Items without labels are prohibited from sale.
4. G-Mark (Gulf Conformity Mark)
A unified conformity mark for Gulf countries. Required for electronics, children’s products, and other sensitive goods.
5. SFDA Certification
Separate approval is required for food, beverages, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and medical devices.
6. Eco-Standards and Fire Safety
Under Vision 2030, special attention is paid to environmental compliance and safety. Construction materials, cables, and textiles undergo additional testing.
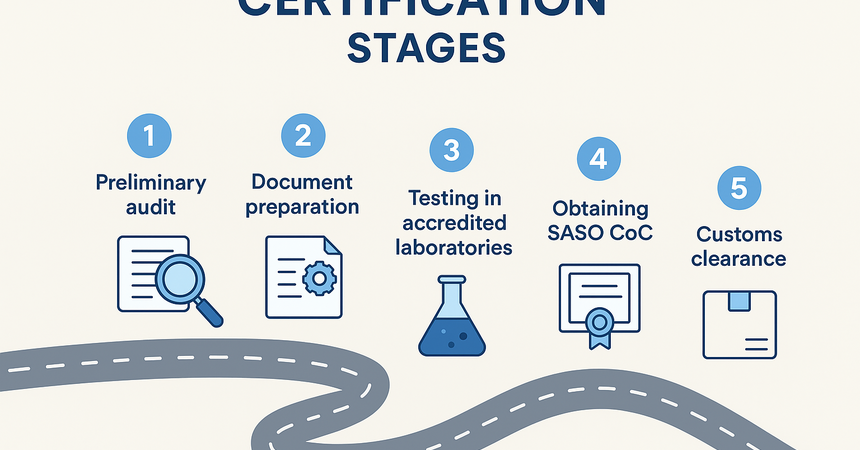
Certification Stages
- Preliminary audit – determining which standards and certificates apply to your product category.
- Document preparation – technical datasheets, test reports, ISO or CE certificates.
- Testing in accredited laboratories – depending on the product category.
- Obtaining SASO CoC and uploading it to the SABER system.
- Customs clearance and market access.
Timing and Costs
- On average, certification takes from 2 weeks to 3 months.
- Costs depend on product category, scope of testing, and documentation volume.
- Errors in paperwork may result in registration refusal or shipment delays at customs.
Risks Without Certification
- Import ban into the Kingdom.
- Fines and product confiscation.
- Loss of reputation among local distributors and investors.
Opportunities for Certified Companies
- Participation in large tenders and government procurement.
- Access to a market of over 36 million people with high purchasing power.
- Long-term partnerships with local companies and involvement in Vision 2030 projects.
Conclusion
Certification is not a mere formality but a strategic tool for entering the Saudi Arabian market. Without it, deliveries are impossible, but with the right approach, certification becomes a competitive advantage that opens the door to the region’s largest contracts.Contact WorldWideBridge – we provide full-cycle certification services for your products and ensure confident entry into the Saudi Arabian market.