Why SABER certification is necessary and what types exist
The SABER system was implemented by Saudi Arabia to control the safety and quality of products entering the local market. Different types of conformity assessment schemes are defined depending on the product's risk level and technical regulations. The two most common schemes are Type 1A and Type 3.
Choosing the correct type of certification directly affects approval timelines and market access.
What is Type 1A certification and when is it used
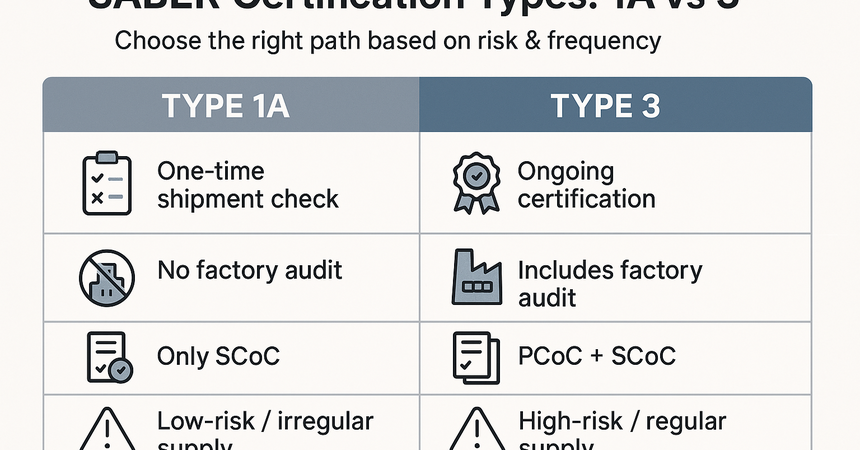
Type 1A certification (Inspection of a single shipment) is a one-time inspection applied to a specific shipment. It is generally used for low-risk products or for occasional imports.Key features of Type 1A:
- Each shipment is individually inspected.
- Only a Shipment Certificate of Conformity (SCoC) is issued; there is no regular Product Certificate of Conformity (PCoC).
- No factory audit is required.
- Commonly used for one-off shipments, customized orders, or products not intended for mass distribution.
What is Type 3 certification and how is it carried out
Type 3 is a more stringent and comprehensive certification scheme. It includes factory assessment, product sample testing, and continuous surveillance.
Key features of Type 3:
- Evaluation of production processes and quality management systems (such as ISO 9001 compliance).
- Product testing to ensure compliance with applicable standards and technical regulations.
- A Product Certificate of Conformity (PCoC) is issued, usually valid for one year (sometimes up to three years).
- A Shipment Certificate of Conformity (SCoC) is also required for each shipment, but the procedure is simplified since the product has already been assessed.
How to choose the right type of certification for your product
Choosing the correct scheme depends on several factors:
- Product category and risk level: Type 1A is often chosen for low-risk products, Type 3 for higher-risk categories.
- Planned shipment frequency: Type 3 is more cost-effective for regular shipments.
- Technical regulation requirements or buyer’s specifications: sometimes a specific type is mandated.
- Manufacturer’s readiness for factory audits and additional testing.